Development History Of L Ergothioneine Powder
l ergothioneine powder, a unique amino acid with potent antioxidant properties, has gained significant attention in the scientific community over the past century.

When was L-ergothioneine first discovered?
The story of L ergothioneine begins in the early 20th century. In 1909, Charles Tanret, a French pharmacist and chemist, first isolated this compound from ergot, a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. Tanret named the substance "ergothioneine" due to its origin and its sulfur-containing structure.
Initially, the significance of this discovery was not fully understood. It wasn't until several decades later that scientists began to unravel its unique properties and potential benefits. The compound's ability to act as a powerful antioxidant and its presence in various organisms sparked curiosity among researchers, leading to further investigations.

How has L ergothioneine powder evolved over time?
The evolution of L ergothioneine powder is closely tied to advancements in scientific understanding and technological capabilities. In the early days following its discovery, pure l ergothioneine was primarily studied in its natural form, extracted from fungal sources. However, as research progressed, scientists developed more sophisticated methods for isolating and purifying the compound.
A significant breakthrough came in the 1950s when researchers successfully synthesized L ergothioneine in the laboratory. This development opened up new possibilities for studying the compound's properties and potential applications. The ability to produce synthetic ergothioneine allowed for more controlled experiments and paved the way for its use in various fields, including medicine and nutrition.
As analytical techniques improved, scientists were able to detect ergothioneine in a wide range of organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals. This discovery led to a better understanding of its distribution in nature and its role in biological systems. Researchers found that while humans cannot synthesize ergothioneine, we have a specific transporter protein (OCTN1) that actively absorbs and retains it, suggesting its importance in human health.
In recent years, the production of L ergothioneine powder has become more sophisticated and efficient. Modern biotechnology techniques have enabled the large-scale production of high-purity ergothioneine through fermentation processes. This has made it more accessible for research and commercial applications, including its use as a dietary supplement and ingredient in skincare products.
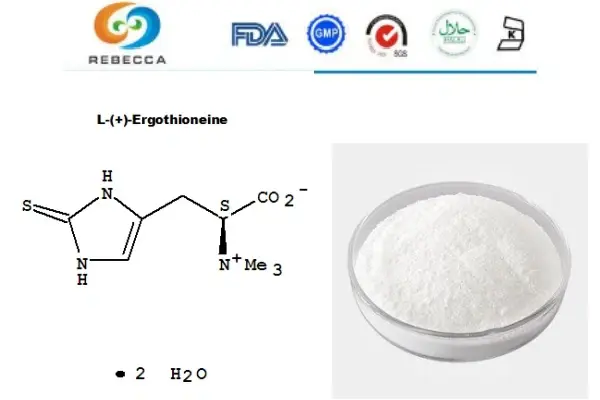
What are the milestones in L-ergothioneine research?
1. 1909: Charles Tanret isolates and identifies L-ergothioneine from ergot fungus.
2. 1950s: Successful laboratory synthesis of ergothioneine, enabling more extensive research.
3. 1960s-1970s: Researchers discover its potent antioxidant properties, sparking interest in its potential health benefits.
4. 2005: Identification of the OCTN1 transporter protein in humans, specifically designed to absorb and distribute L-ergothioneine throughout the body. This discovery suggested that pure l ergothioneine might play a crucial role in human health.
5. 2010s: Multiple studies demonstrate its potential neuroprotective effects, suggesting its possible role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
6. 2016: A large-scale population study in Singapore links higher mushroom consumption (a primary dietary source) with reduced risk of cognitive decline in older adults.
7. 2018: Renowned biochemist Bruce Ames classifies Lergothioneine as a potential "longevity vitamin," highlighting its importance in promoting healthy aging.
8. 2020: Clinical trials begin to investigate the effects of ergothioneine supplementation on various health outcomes, including cognitive function and cardiovascular health.
These milestones represent significant advancements in understanding pure l ergothioneine and its potential applications. As research continues, we can expect to see further developments in the production and utilization of L ergothioneine powder in various fields, from nutraceuticals to pharmaceuticals.
The journey from its initial discovery to its current status as a promising health-promoting compound is a testament to the power of scientific inquiry and technological progress. As we continue to unlock the secrets of this unique amino acid, it's clear that L ergothioneine powder will play an increasingly important role in our quest for better health and longevity.

L-Ergothioneine Powder Manufacturer
As the importance of L-ergothioneine continues to grow, the demand for high-quality, pure l ergothioneine has increased significantly. Rebecca Bio-Tech has emerged as a leading manufacturer in this field, meeting the needs of various industries with its premium product.
Rebecca Bio-Tech is a professional L ergothioneine powder manufacturer based in China, with an impressive yearly production quantity of more than 30,000 kgs. Our state-of-the-art facilities and rigorous quality control measures ensure that we consistently produce pure L-ergothioneine powder that meets the highest industry standards.
Whether in the nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, or food and beverage industry, Rebecca Bio-Tech is equipped to meet your ergothioneine powder needs. We offer customizable solutions to your specific requirements, backed by our extensive experience and expertise in its production.
For more product information, to request samples, or to discuss your custom requirements, please don't hesitate to contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References:
- Tanret, C. (1909). Sur une base nouvelle retirée du seigle ergoté, l'ergothionéine. Compt. Rend, 149, 222-224.
- Cheah, I. K., & Halliwell, B. (2012). Ergothioneine; antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1822(5), 784-793.
- Melville, D. B. (1959). Ergothioneine. Vitamins & Hormones, 17, 155-204.
- Heath, H., & Wildy, J. (1956). The biosynthesis of ergothioneine and histidine by Claviceps purpurea: I. The incorporation of [2-14C] acetate. Biochemical Journal, 64(4), 612.
- Gründemann, D., Harlfinger, S., Golz, S., Geerts, A., Lazar, A., Berkels, R., ... & Schömig, E. (2005). Discovery of the ergothioneine transporter. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(14), 5256-5261.
- Bello, M. H., Barrera-Perez, V., Morin, D., & Epstein, L. (2012). The Neurospora crassa mutant NcΔEgt-1 identifies an ergothioneine biosynthetic gene and demonstrates that ergothioneine enhances conidial survival and protects against peroxide toxicity during conidial germination. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 49(2), 160-172.








