Extraction Technology of Gastrodin
gastrodin powder is a key bioactive compound found in the traditional Chinese herb Gastrodia elata. As interest in this compound grows, so does the need for efficient and effective extraction methods.
Its extraction is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail and a deep understanding of the compound's chemical properties.

Raw Material Processing And Preliminary Extraction
The extraction process for gastrodin powder begins with the careful selection and processing of the raw material, typically the rhizomes of Gastrodia elata.
First, the Gastrodia elata rhizomes are harvested at the optimal time, usually after 2-3 years of growth when the gastrodin content is at its peak. The rhizomes are at that point cleaned completely to expel any dirt, debris or other impurities that might meddled with the extraction prepare or compromise the immaculateness of the last item. Upon cleaning, the rhizomes are typically dried to reduce moisture content and prevent degradation. This drying process can be carried out through natural means, such as the sun, or using controlled-temperature drying chambers. The dried rhizomes are then ground into a fine powder to increase the surface area and improve extraction efficiency.
The preliminary extraction of gastrodin from the powdered rhizomes often involves a process called solid-liquid extraction. This method uses a solvent, typically water or a water-alcohol mixture, to dissolve the gastrodin and other water-soluble compounds from the plant material.
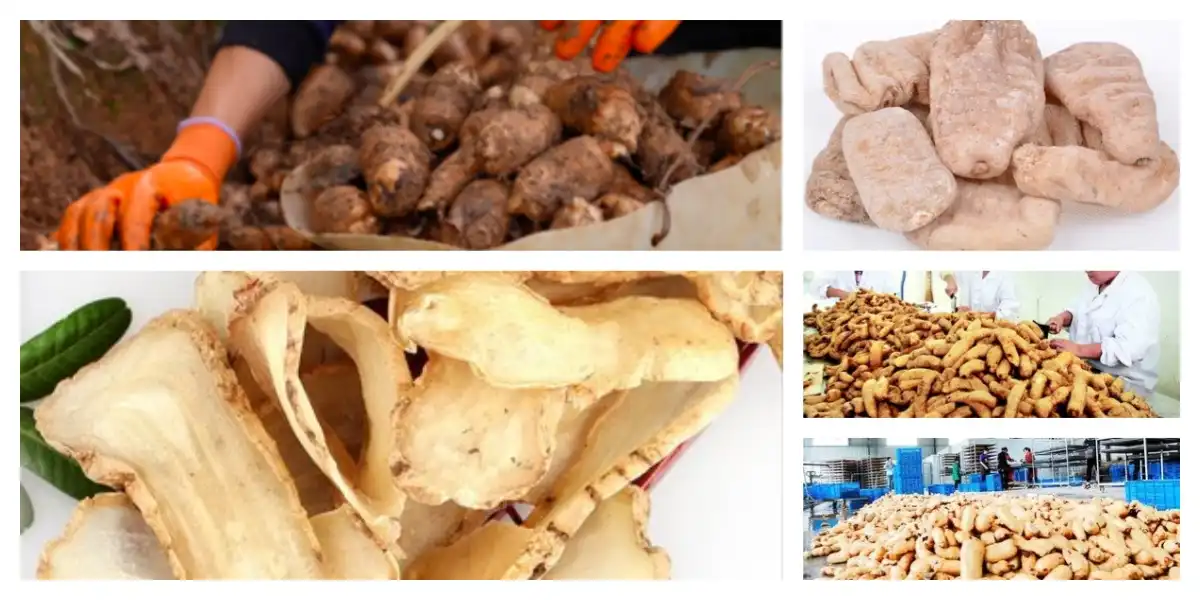

One common method for this initial extraction is reflux extraction. In this process, the powdered rhizomes are mixed with the solvent and heated to the solvent's boiling point. The vapor is then cooled and condensed back into the extraction vessel, creating a continuous cycle that efficiently extracts the desired compounds.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction has gained widespread popularity in recent years. This technique uses high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic bubbles in the solvent, which collapse and create localized areas of high temperature and pressure. This process, known as cavitation, can significantly improve the efficiency of extraction by breaking down cell walls and enhancing mass transfer.
Regardless of the specific method used, the result of this preliminary extraction is a crude extract containing gastrodin along with various other compounds from the Gastrodia elata rhizomes. This crude extract then moves on to the next stage of the process: purification.
Crude Extract Purification
The crude extract obtained from the initial extraction process contains a complex mixture of compounds, including gastrodin, other phenolic compounds, polysaccharides, and various plant metabolites. The goal of the purification stage is to separate gastrodin from these other compounds, increasing its concentration and purity.
One of the primary methods used for crude extract purification is liquid-liquid extraction. This process exploits the different solubilities of compounds in two immiscible liquids, typically an aqueous solution and an organic solvent.
Another crucial purification technique is column chromatography. In this method, the crude extract is subjected to a column filled with a stationary phase, often silica gel or a specialized resin. Different compounds in the extract interact with the stationary phase to varying degrees, causing them to move through the column at different rates. This allows for the separation of gastrodin from other compounds based on their physical and chemical properties.
In recent years, more advanced chromatographic techniques have been employed for gastrodin purification. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and preparative HPLC offer high resolution and efficiency in separating gastrodin from other compounds. These methods can provide very pure gastrodin powder, although they are often more expensive and time-consuming than traditional purification methods.
Each step in the purification process increases the concentration and purity of gastrodin, bringing us closer to the final refined product.
Refining And Finished Product Preparation
After the purification stage, the gastrodin extract undergoes further refining to achieve the desired purity and form for the finished product.
Crystallization is one of the primary refining techniques. In this process, the purified gastrodin solution is carefully concentrated and cooled under controlled conditions, causing gastrodin crystals to form. Upon separation of these crystals from the remaining solution, a highly pure form of gastrodin can be achieved.
The crystallization process may be repeated multiple times to achieve higher levels of purity. Following crystallization, the crystals typically undergo a drying process to remove any residual moisture.
Throughout the refining and finished product preparation stage, strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure the purity , potency, and consistency of the gastrodin powder. This includes regular testing using analytical techniques such as HPLC or mass spectrometry to verify the gastrodin content and detect any impurities.
Quality Control
One of the key components of quality control in Gastrodin powder is the use of analytical techniques to monitor the purity and concentration of gastrodin at various stages of the process.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is widely used for this purpose, allowing for precise quantification of gastrodin and detection of impurities. Other analytical methods such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy may also be employed for more detailed analysis of the extract composition.
In addition to chemical analysis, physical characteristics of the extract and final product are also closely monitored. This includes parameters such as moisture content, particle size distribution, and solubility.
About Rebecca Bio-Tech
Rebecca Bio-Tech has established itself as a leader in the field of natural extract production and research, with a particular focus on high-purity Gastrodin extraction. The company's commitment to quality and innovation is exemplified by its hotsale product: high purity Gastrodin 99%.
Rebecca Bio-Tech's high-purity Gastrodin powder is particularly valuable for researchers and pharmaceutical companies working on developing new therapies based on this compound. The high purity ensures that experimental results are not confounded by the presence of impurities, allowing for more accurate and reliable research outcomes.
For those interested in learning more about Rebecca Bio-Tech's high purity Gastrodin 99% or their other products and services, the company welcomes inquiries. They can be contacted at information@sxrebecca.com for further information. This open line of communication demonstrates Rebecca Bio-Tech's commitment to transparency and customer service, allowing potential clients or research partners to engage directly with the company and learn more about their products and processes.
References
1. Zhang, Y., Li, M., Kang, R. X., Shi, J. G., Liu, G. T., & Zhang, J. J. (2012). NHBA isolated from Gastrodia elata exerts sedative and hypnotic effects in sodium pentobarbital-treated mice. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 102(3), 450-457.
2. Chen, P. J., Hsieh, C. L., Su, K. P., Hou, Y. C., Chiang, H. M., Lin, I. H., & Sheen, L. Y. (2009). The antidepressant effect of Gastrodia elata Bl. on the forced-swimming test in rats. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, 37(03), 503-514.
3. Huang, N. K., Chern, Y., Fang, J. M., Lin, C. I., Chen, W. P., & Lin, Y. L. (2007). Neuroprotective principles from Gastrodia elata. Journal of Natural Products, 70(4), 571-574.
4. Liu, Y., Gao, J., Peng, M., Meng, H., Ma, H., Cai, P., ... & Xu, Z. (2018). A review on central nervous system effects of gastrodin. Frontiers in pharmacology, 9, 24.








